Lightning Framework is a new undetected Swiss Army Knife-like Linux malware that has modular plugins and the ability to install rootkits.
Year after year Linux environments increasingly become the target of malware due to continued threat actor interest in the space. Malware targeting Linux environments surged in 2021, with a large amount of innovation resulting in new malicious code, especially in ransomwares, trojans, and botnets. With the rise in use of the cloud, it is no wonder that malware innovation is still accelerating at breakneck speed in this realm.
This is a technical analysis of a previously undocumented and undetected Linux threat called the Lightning Framework. It is rare to see such an intricate framework developed for targeting Linux systems. Lightning is a modular framework we discovered that has a plethora of capabilities, and the ability to install multiple types of rootkit, as well as the capability to run plugins. The framework has both passive and active capabilities for communication with the threat actor, including opening up SSH on an infected machine, and a polymorphic malleable command and control configuration. We are releasing this blog for informational purposes. We do not have all the files that are referenced in the framework, but hope that this release will help others if they possess other pieces of the jigsaw puzzle. We have not observed this malware being used in attacks in the wild.
Technical Analysis of Lightning Framework
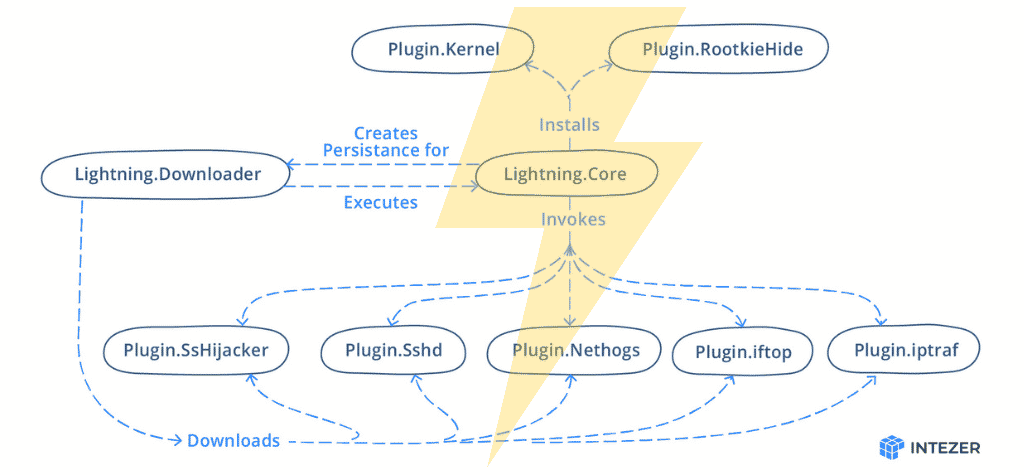
The framework consists of a downloader and core module, with a number of plugins. Some of the plugins used by the malware are open-source tools. Below is a figure of the framework layout:
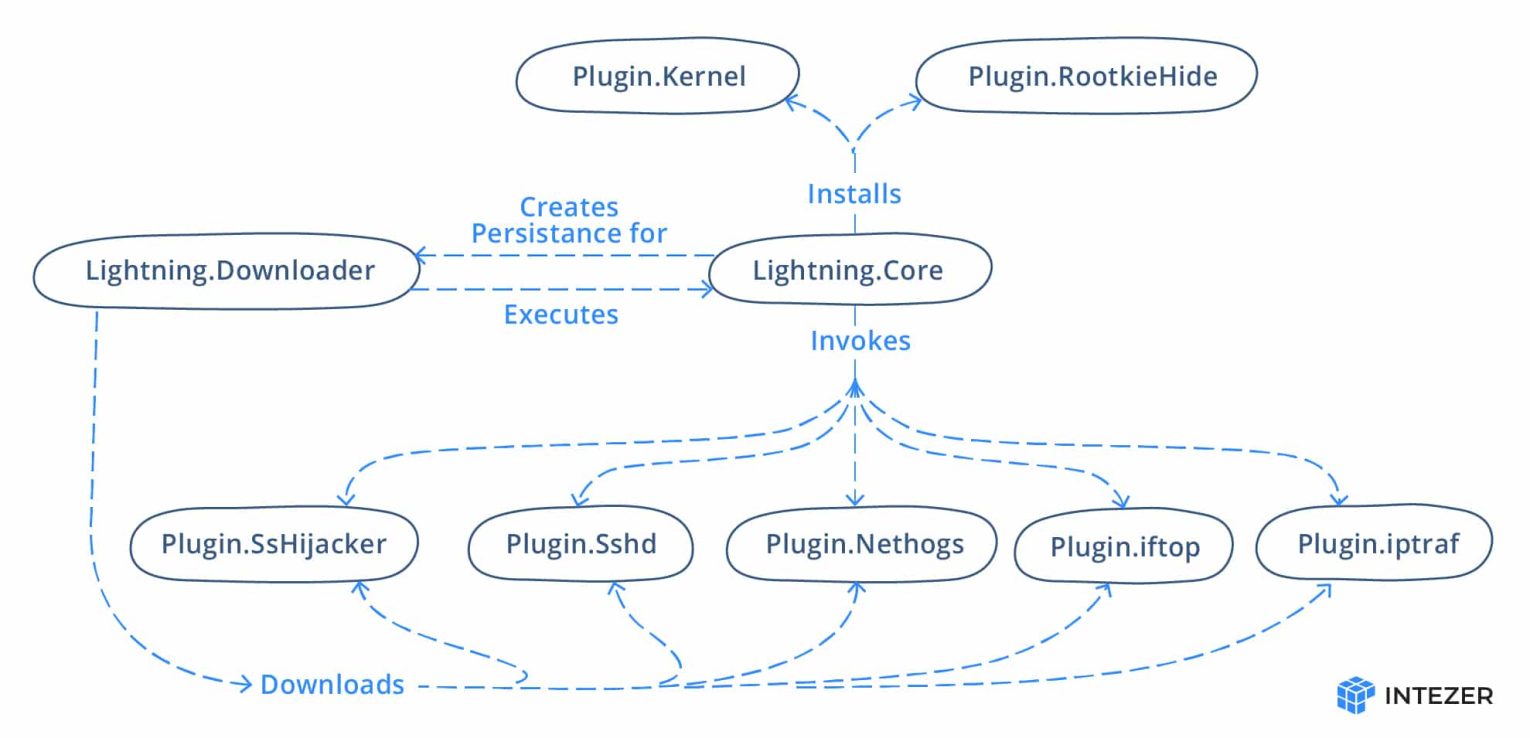
Overview of the Modules
| Name | Name on Disk | Description |
| Lightning.Downloader | kbioset | The persistent module that downloads the core module and its plugins |
| Lightning.Core | kkdmflush | The main module of the Lightning Framework |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.SsHijacker | soss | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd | sshod | OpenSSH with hardcoded private and host keys |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Nethogs | nethoogs | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. Presumably the software Nethogs |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.iftop | iftoop | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. Presumably the software iftop |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.iptraf | iptraof | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. Presumably the software IPTraf |
| Linux.Plugin.RootkieHide | libsystemd.so.2 | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. LD_PRELOAD Rootkit |
| Linux.Plugin.Kernel | elastisearch.ko | There is a reference to this module but no sample found in the wild yet. LKM Rootkit |
Lightning.Downloader
The main function of the downloader module is to fetch the other components and execute the core module.
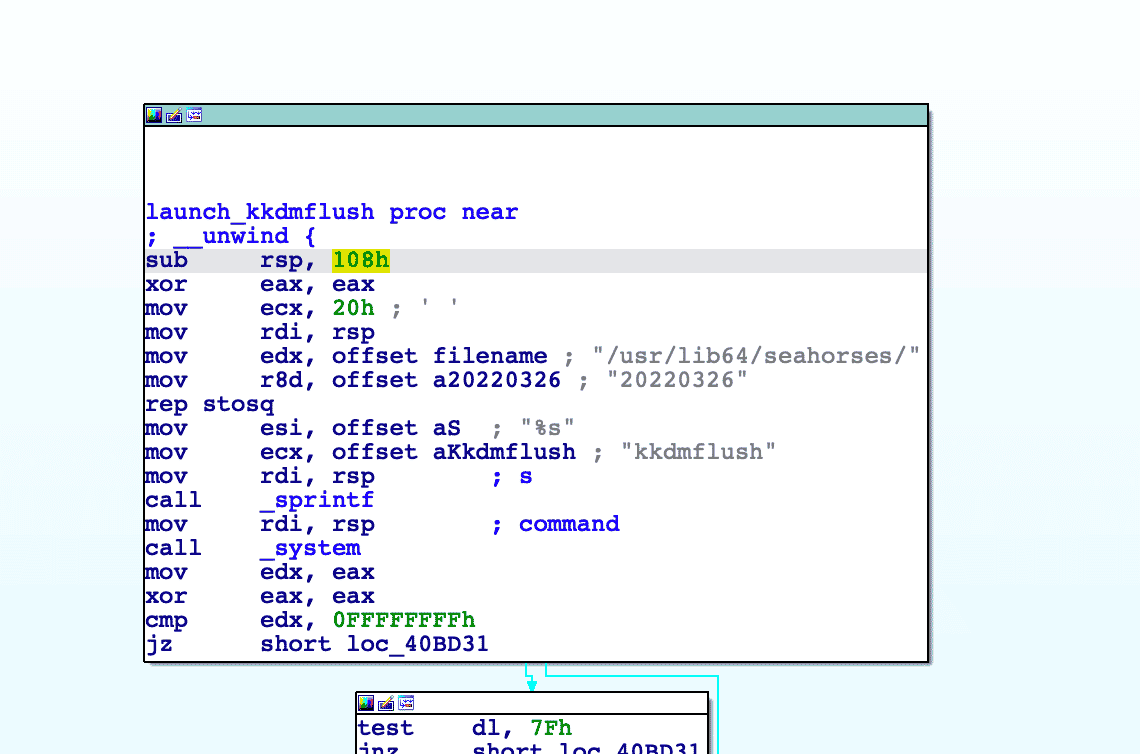
The downloader module starts by checking if it is located in the working directory /usr/lib64/seahorses/ under the name kbioset. The framework makes heavy use of typosquatting and masquerading in order to remain undetected. The reference to seahorses masquerades the password and key manager software seahorse. If not it will relocate itself to that working directory and execute that copy. The downloader will fingerprint the host name and network adapters to generate a GUID, which will be sent to the command and control (C2) server.
The downloader will then contact the C2 to fetch the following modules and plugins:
- Linux.Plugin.Lightning.SsHijacker
- Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd
- Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Nethogs
- Linux.Plugin.Lightning.iftop
- Linux.Plugin.Lightning.iptraf
- Lightning.Core
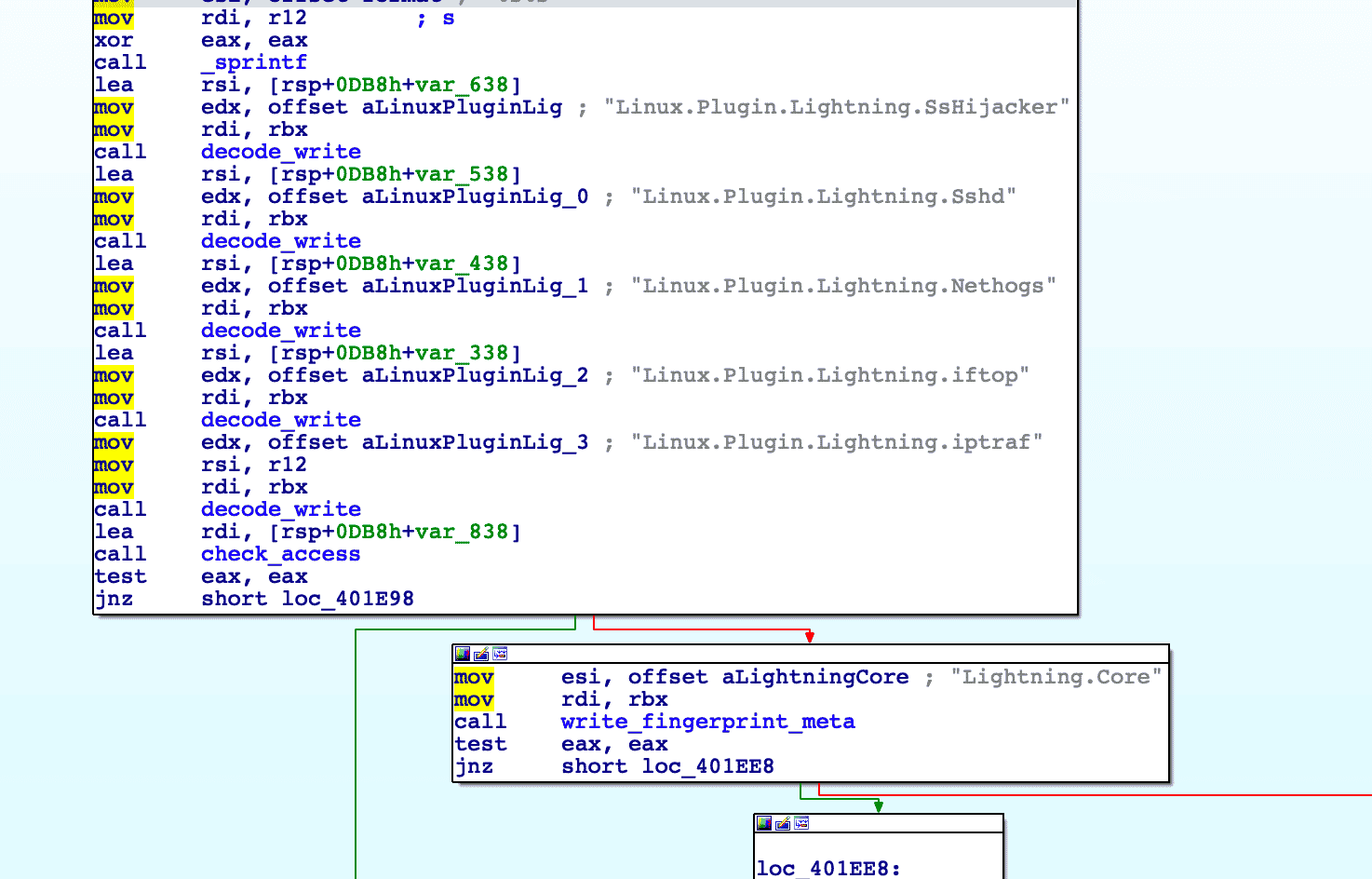
The method of contacting the C2 will be described below in the malleable C2 section (click here to jump to that section). The downloader will then execute the core module (kkdmflush).
Lightning.Core
The core module is the main module in this framework, it is able to receive commands from the C2 and execute the plugin modules. The module has many capabilities and uses a number of techniques to hide artifacts to remain running under the radar.
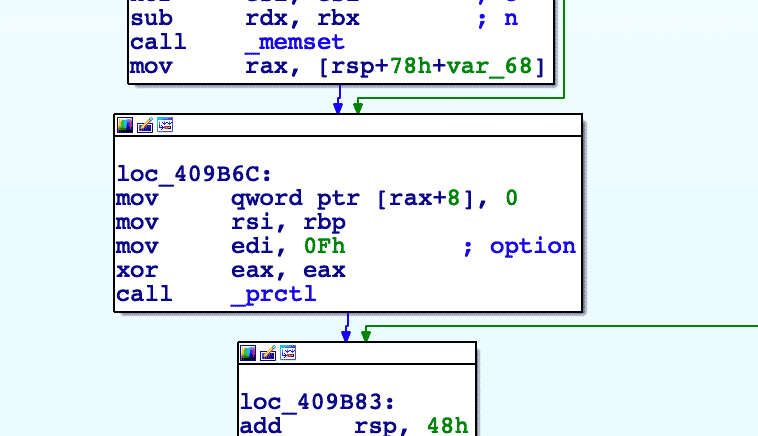
The core module modifies the name of the calling thread of the module to kdmflush, to make it appear that it is a kernel thread.
Next the core module sets up persistence by creating a script that is executed upon system boot. This is achieved by first creating a file located at /etc/rc.d/init.d/elastisearch. The name appears to typosquat elasticsearch. The following contents are written to the file:
#!/bin/bash
# chkconfig:2345 90 20
/usr/lib64/seahorses/kbioset &This script will execute the downloader module upon boot. The service is then added using the chkconfig utility.

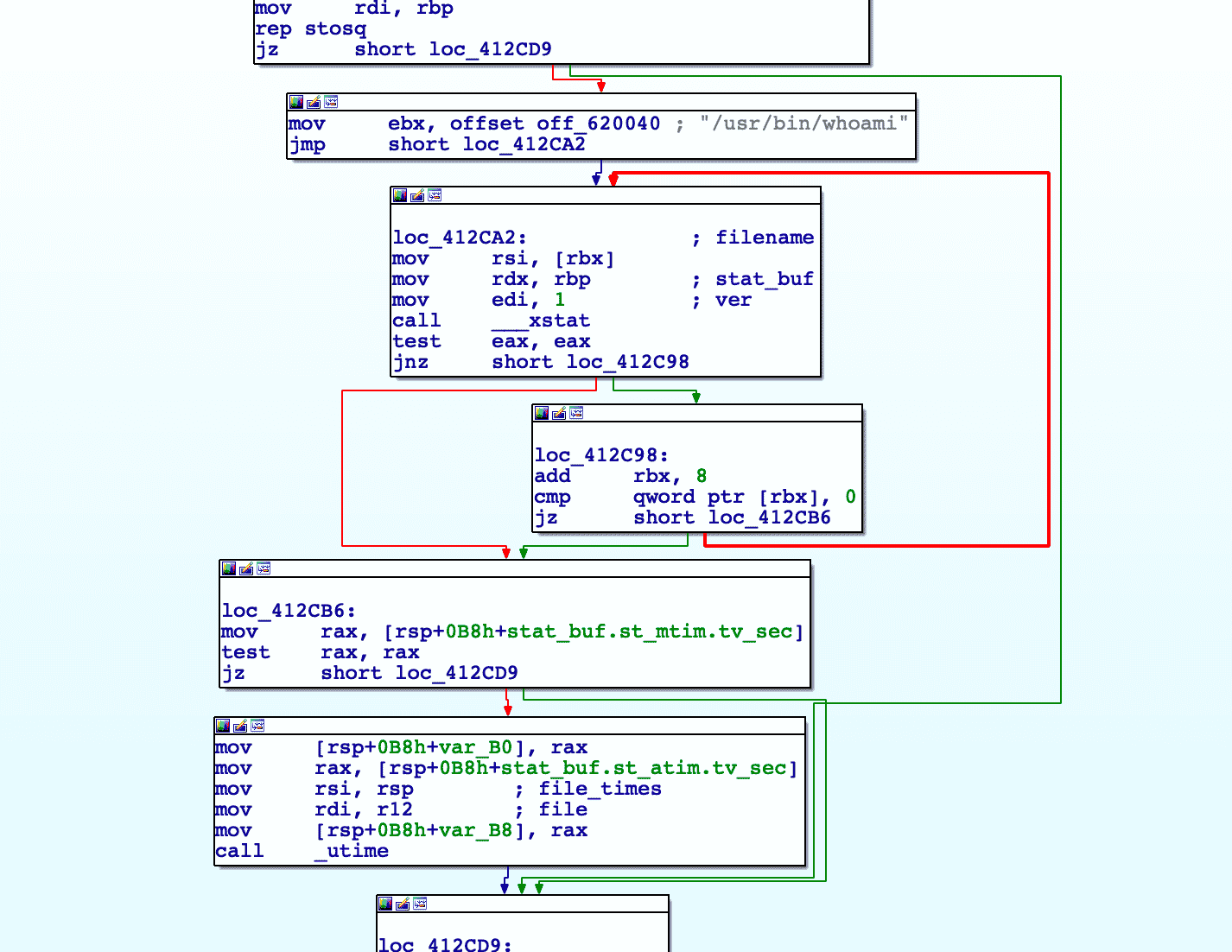
The timestamp of the file is modified to hide artifacts, a technique known as “timestomping”. The file has its last modified time edited to match that of either whoami, find, or su. It will look for each file respectively until it finds one. This technique is used for most of the files that the framework creates.
The malware will attempt to hide its Process ID (PID) and any related network ports. This is achieved by writing the frameworks running PIDs to two files: hpi and hpo. These files are parsed and then the existence of the file proc/y.y is checked. If the file exists, it means that a rootkit has been installed. The PIDs are written to proc/y.y for use by the rootkit, which may scrub any reference to files running in the framework from commands such as ps and netstat.
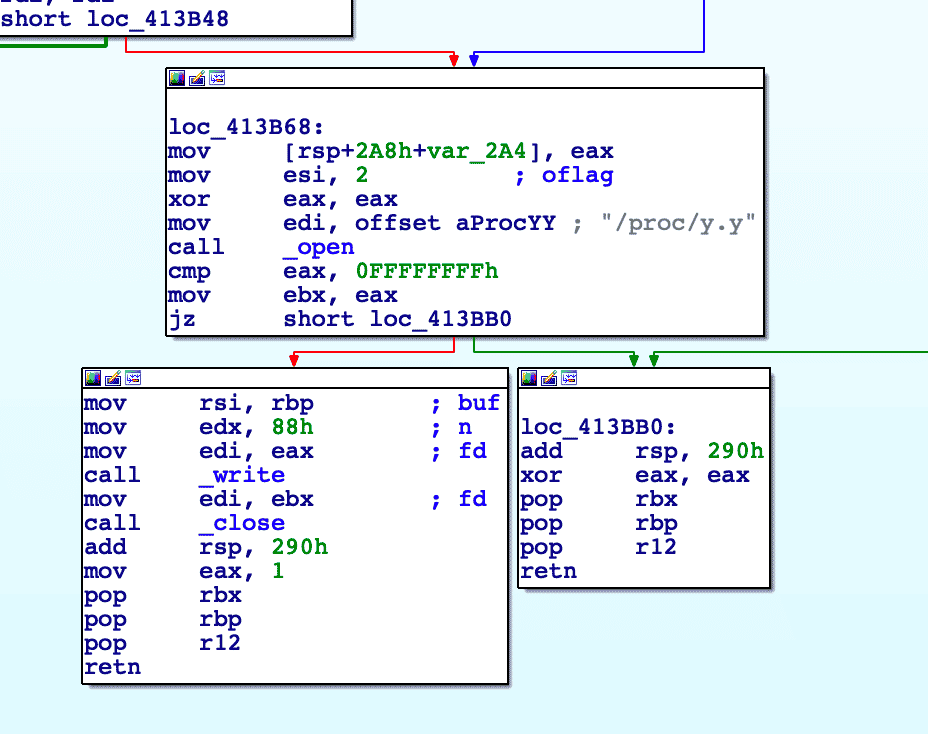
The core module will generate a GUID in the same manner as the downloader and contact the C2. The response is parsed and the command is executed. The core module has the following commands:
| Command | Description |
| SystemInfo | Fingerprints the machine |
| PureShellCommand | Runs Shell command |
| RunShellPure | Starts the Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd (SSH Daemon) plugin |
| CloseShellPure | Terminates the Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd plugin |
| Disconnect | Exits the Core module |
| GetRemotePathInfo | Collects the summary of given path |
| KeepAlive | No action, connection remains alive |
| UploadFileHeader | Checks access of file |
| FileEdit | Gets contents of file and time meta |
| TryPassSSH | Adds a public key to the root/.ssh/authorized_keys file |
| DeleteVecFile | Deletes the specified file or path |
| PreDownloadFile | Calculates a checksum of the file |
| DownloadFile | Sends a file to the C2 |
| DeleteGuid | Removes the framework |
| UpdateVersion | Calls the Downloader module to update the framework |
| UpdateRemoteVersion | Updates the framework including the downloader |
| Socks5 | Sets up a Socks5 proxy |
| RestorePlug | The same as UpdateVersion |
| GetDomainSetting | Fetches the contents of the malleable C2 configuration file (cpc) |
| SetDomainSetting | Updates the contents of the malleable C2 configuration file (cpc) |
| InstallKernelHide | Fetches the OS release |
| RemoveKernelHide | Removes kernel module |
| UpdateKernelVersion | Removes the kernel module and runs uname -r |
| OverrideFile | Overwrites specified file |
| UploadFileContent | Writes data sent from server to file |
| LocalPluginRequest | Either write the LD_PRELOAD rootkit or LKM rootkit |
Network Communication
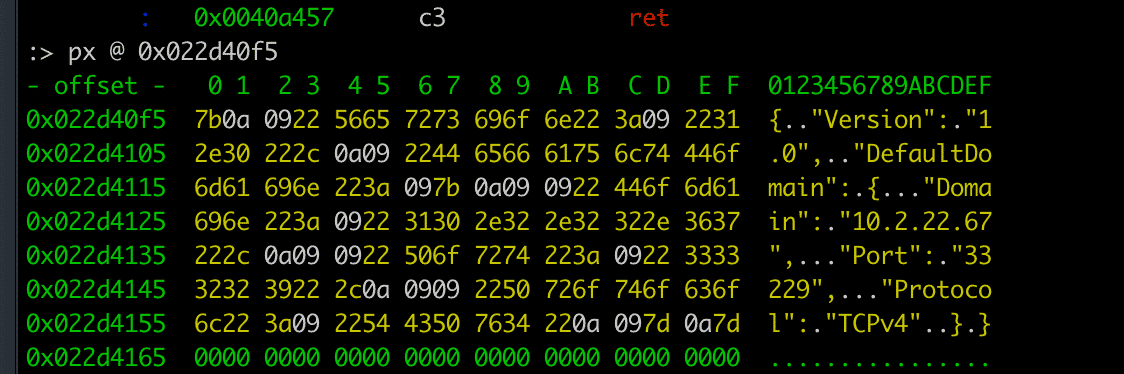
Network communication in the Core and Downloader modules are performed over TCP sockets. The data is structured in JSON. The C2 is stored in a polymorphic encoded configuration file that is unique for every single creation. This means that configuration files will not be able to be detected through techniques such as hashes. The key is built into the start of the encoded file.
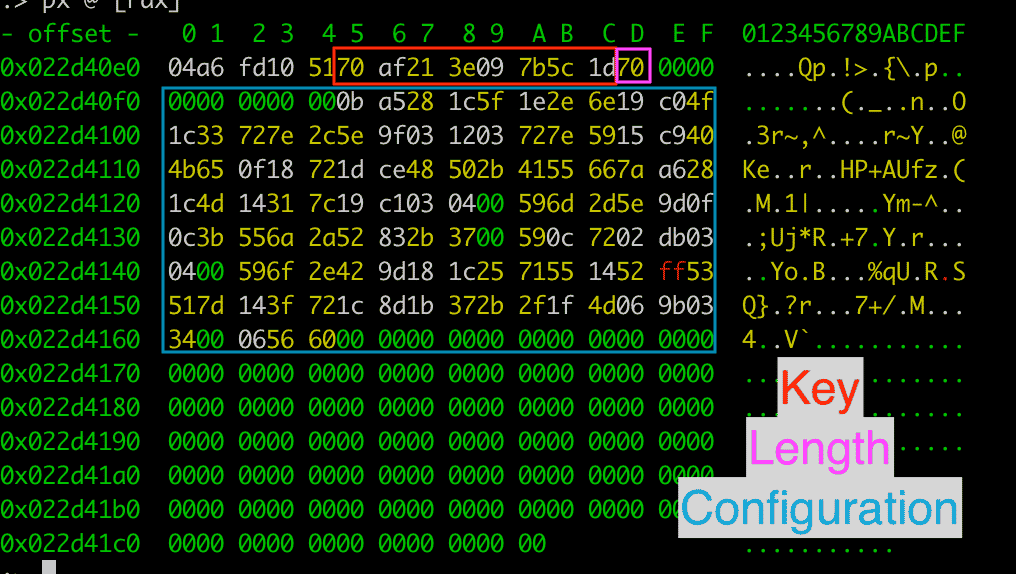
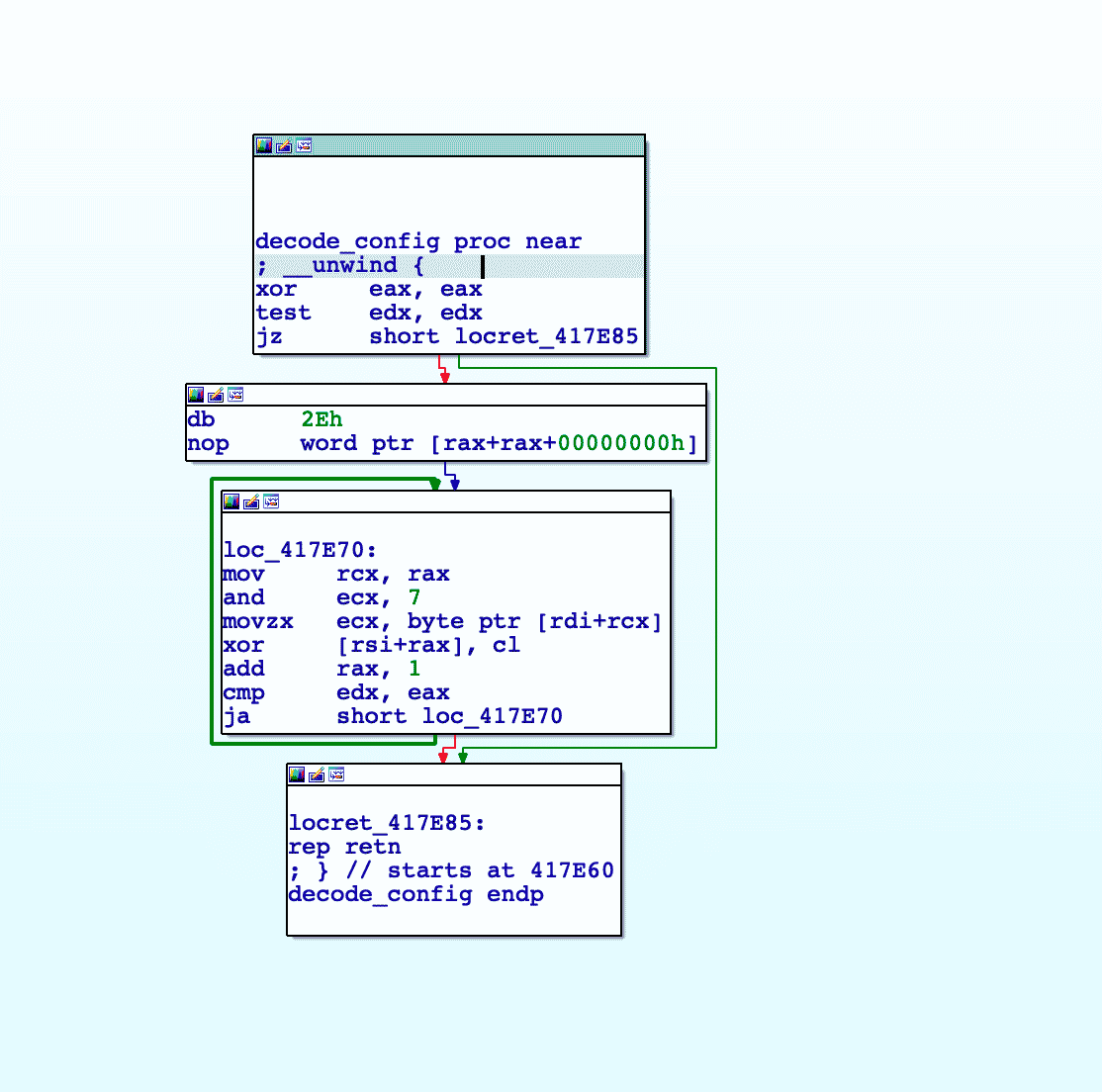
The decoded configuration is structured in JSON. The default configuration in the analyzed sample uses a local IP address 10.2.22[.]67 with the port 33229.
There is a passive mode of communication available if the actor executes the RunShellPure command. This starts an SSH service on the infected machine with the Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd plugin. The plugin is an OpenSSH daemon that has hardcoded private and host keys, allowing the attacker to SSH into the machine with their own SSH key, creating a secondary backdoor.

Summary
The Lightning Framework is an interesting malware as it is not common to see such a large framework developed for targeting Linux. Although we do not have all the files, we can infer some of the missing functionality based on strings and code of the modules that we do possess. Check out our next blog here about detection opportunities for Lightning Framework using osquery.
We would like to extend a huge thanks to our friends and partners at IBM and SentinelOne for their help during investigating this threat.
IOCs for Lightning Framework
Hashes
| File | SHA256 |
| Lightning.Downloader | 48f9471c20316b295704e6f8feb2196dd619799edec5835734fc24051f45c5b7 |
| Lightning.Core | fd285c2fb4d42dde23590118dba016bf5b846625da3abdbe48773530a07bcd1e |
| Linux.Plugin.Lightning.Sshd | ad16989a3ebf0b416681f8db31af098e02eabd25452f8d781383547ead395237 |
Sigma Detection Rules
title: Lightning Framework File Path
status: experimental
description: Detects creation of files related to Lightning Framework.
author: Intezer
references:
- https://intezer.com
logsource:
product: linux
category: file_create
detection:
selection1:
TargetFilename|startswith:
- '/usr/lib64/seahorses/'
selection2:
TargetFilename|contains:
- 'kbioset'
- 'cpc'
- 'kkdmflush'
- 'soss'
- 'sshod'
- 'nethoogs'
- 'iftoop'
- 'iptraof'
condition: selection1 and selection2
falsepositives:
- Unknown.title: Lightning Default C2 Communication
status: experimental
description: Detects communication to default local ip for Lightning Framework
author: Intezer
references:
- https://intezer.com
logsource:
category: firewall
detection:
select_outgoing:
dst_ip: 10.2.22.67
dst_port: 33229
condition: select_outgoing
falsepositives:
- Unknown. MITRE ATT&CK
| Tactic | Technique | ID | Description |
| Persistence | Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts | T1037 | An init.d script is used for persistence of downloader module |
| Persistence | SSH Authorized Keys | T1098.004 | SSH keys can be added to the authorized_keys file |
| Defense Evasion | Obfuscated Files or Information | T1027 | The C2 profile is encoded on disk |
| Defense Evasion | Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | T1140 | The C2 profile is decoded with a dynamic XOR algorithm |
| Defense Evasion | Hide Artifacts | T1564 | Many artifacts are hidden including ports, PIDs, and file timestamps |
| Defense Evasion | Masquerading | T1036 | Many files are masqueraded as other files or tasks |
| Defense Evasion | Rootkit | T1014 | LKM and LD_PRELOAD rootkits are used |
| Defense Evasion | Timestomp | T1070.006 | Files created by Lightning are modified to match that of other utilities |
| Defense Evasion | File Deletion | T1070.004 | The framework has the ability to remove itself |
| Discovery | File and Directory Discovery | T1083 | The framework can list files and directories on infected systems |
| Discovery | Network Service Discovery | T1046 | Multiple plugins can be used to perform network service discovery |
| Discovery | Network Sniffing | T1040 | Multiple plugins can be used to perform network sniffing |
| Discovery | System Information Discovery | T1082 | Lightning can perform detailed system fingerprinting |
| Command and Control | Data Encoding | T1132 | Data from the C2 is encoded |
| Command and Control | Non-Application Layer Protocol | T1095 | Communication with the C2 is performed over TCP |
| Command and Control | Proxy | T1090 | The framework has the ability to start a Socks5 proxy |
| Command and Control | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | T1041 | Data can be exfiltrated |